When your vehicle engine knocks, it means that it produces pinging, knocking or banging sounds. This is usually caused by unusual combustion of the mixture of air as well as fuel and it can very upsetting and dangerous. Hence, it is very essential for you to know how to test for engine knock so that you will be able to fix the problem in good time.
In this article, you will get access to information on ways to discover knocking, how it happens, what causes engine knock and how to fix engine knock. You will have a great time reading this piece. Enjoy!
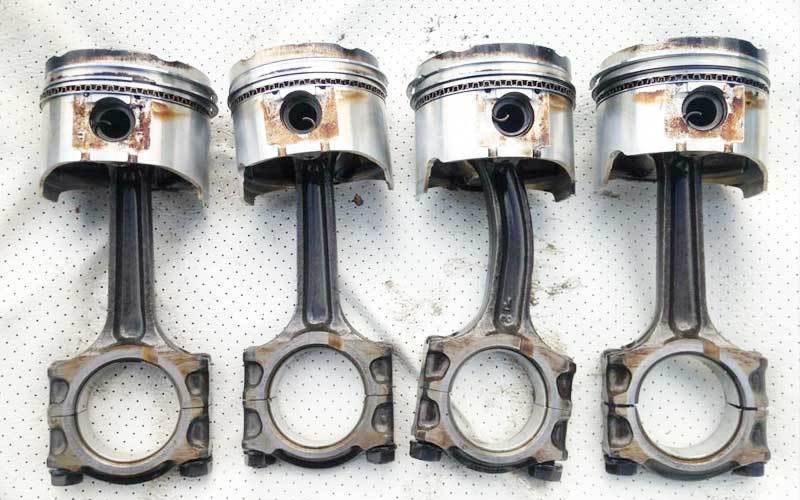

Connecting rod knock
How Engine Knock Happens
There are four major causes of engine knock including engine overheating, ignition timing that is overly advanced, accumulation of carbon in the combustion cylinders or chamber and the usage of lower octane fuel, which is not in line with what is recommended for you.
In addition, faulty components of one or more systems have the capacity of triggering any of the causes mentioned above. This will go a long way to upset the process of combustion.
The Noise of Faulty Lifters vs. Connecting Rods
In order to test for engine knock, you need to be sensitive to the sound made by your car. if the hydraulic lifter of your car engine is faulty, you will hear a distinct tapping sound. The rhythm of the tapping sound will be fast and this will usually be heard when your car is hot or cold.
On the other hand, the sound produced by a faulty connecting rod is similar to when somebody bangs on your oil pan using a hammer. As you accelerate, the frequency and pitch of the sound may fade, change or almost disappear. When you don’t accelerate again, the sound may continue or become louder. The noise may reduce when your engine is cold but it is possible that it will return consistently.
Normal and Abnormal Combustion
Usually, normal combustion should begin with the ideal blend of fuel and air. The ignition process of the mixture should begin effortlessly and progressively so that the utmost quantity of pressure can be produced just as the piston travels downward after getting to the top dead center (TDC). This leads to the production of the most effective engine performance.
Alternatively, abnormal combustion upsets the effortless process through the creation of a second ignition cycle which may be created before or after the regular cycle that a spark plug produced. You will hear a knock or pink sound as the second cycle expresses itself. Abnormal combustion has the capacity of blowing the head gasket, damaging a valve, cracking the combustion chamber or cylinder or blowing a hole in the pistol.
What causes engine knock and how to fix engine knock
There are some common system or part faults which can lead to knocking of your car engine. In understanding these common faults, you will be able to identify the problem and carry out the proper fixing as soon as possible. Some of them are discussed below.
Engine Overheating
Engine overheating can lead to abnormal combustion and it is also possible for overheating to be triggered in so many ways. You should inspect the coolant level as well as radiator for clogging.
The operation of the fan cooling the engine should be verified and antifreeze should be replaced in accordance to the manufacturer’s schedule. You can use the repair manual of your vehicle to properly check the system if any overheating is noticed.
Ignition Timing Too Advanced
You should inspect the ignition timing of your vehicle in accordance with its repair manual. If your manual is lost or you don’t have at all, you can purchase a cheap aftermarket manual.
If the engine comes with a distributor, you can try to adjust its timing by disengaging and turning the distributor around. On state-of-the-art vehicle engines with OBD II systems, you should investigate if the sensors controlling ignition timing require replacements.
Carbon Buildup
Carbon deposit can be caused by the use of engine oil containing a greater weight than the one suggested by the manufacturer. It can also be brought about when you use fuel of low quality or drive the engine lower than normal operating temperature or you are used to intermittent short trips.
You should inspect the spark plug one by one and if you discover dirty deposits around their electrodes, it may be an indication that there is a carbon build up on the valves and pistons. You can use a flashlight to peek into the spark hole, even though this is very hard to do if you don’t have an endoscope camera.
If you are interested in decarbonizing the chamber, you can use Seafoam or homogenous products. This will help you to clean inner part of the chamber, cylinder, fuel injectors and intake manifold.
Low-Octane Fuel
If you’re using low-octane fuel, you will be giving problems to your engine. A lot of manufacturers produce fuel that have been blended with anti knock additives so that gasoline’s combustion properties will be lowered in order to guard against engine knock.
Octane rating refers to the ability of a particular brand of gasoline to prevent knocking. The higher the rating, the better resistance will be provided against knocking. For example, fuel rated as 87 will not produce better knocking resistance as one rated as 91.
It does not mean that if you get high octane fuel, you are very special. It is advisable to use high-octane fuel for high-compression engines and the lower version for low-compression engines.
In many cases, you can go for a higher octane fuel than the one suggested by the manufacturer and this will serve as a preventive action for your engine. But it is not advisable to use a lower octane fuel than the one recommended by your manufacturer so that you don’t knock your engine.
Incorrect Spark Plugs
Spark plugs come in two ratings, they either be rated as hot or cold. Thee ability of the plug to transfer heat from the combustion chamber to the cooling system remains their vital classification criterion.
The insulator of a hot plug has a larger and longer diameter. Its rate of heat transfer is not as fast a’s compared to a code plug and this helps in clearing away deposits that may want to build up on the plug.
A cold spark plug will ensure that heat is transferred from the engine into the cooling system faster so that pre-ignition and overheating will be prevented. It is very important for you to use the spark plug suggested by your manufacturer in order to prevent engine knock.
Exhaust Backpressure
One of the common problems with exhaust systems is high back pressure. This is caused due to clogged catalytic converter, exhaust pipe or muffler. Exhaust back pressure formation is usually caused by a clogged converter. This will hinder engine airflow making the engine to work at a high temperature and be deprived of power which will eventually lead to knocking.
In order to inspect the exhaust system so that you will be able to discover any high pressure, you can lift the front of your car and place it on your jack stand. The converter should then be tapped with the aid of a rubber mallet and if it jiggles, it is an indication that the catalyst material is reducing to pieces. You can also use a vacuum gauge to check high back pressure.
Vacuum Leaks
Solenoids, actuator and switches in the engine are operated by vehicle emission systems through vacuum. For instance, the manifold absolute pressure (MAP), EGR valve, sensor, purge valve, positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve as well as other components may be operated by vacuum.
When these components experience vacuum leaks, it can lead to spark pinging or knocking. You should inspect these systems’ vacuum hoses for loose connections as well as damage.
Faulty Knock Sensor
Faulty Knock Sensor
Some engines make use of a knock sensor (KS) which assists in detecting the frequency vibrations created by detonation, pre-ignition and knocking. The computer of your car makes use of this information to hinder timing. So when a KS failed, it can bring about pre-ignition as well as knocking.
Knock sensor can be tested by using a wrench or hammer to hit the engine near the sensor when the engine is in an idle mode. When the computer gets the bleep from the KS, you discover that there will be a change in idling RPMs of the engine. You can refer to the repair manual of your vehicle if you think it is exigent.
Takeaways
It is very essential for you to test for engine knock so that you will have the opportunity of preventing a damage to your engine. You must ensure that you diagnose the faults causing abnormal combustion and try as much as possible to fix them before they cause serious problems for your engine. You can use the repair guide of your vehicle to fix the problem and if it is something that you cannot fix, you should not hesitate to see your auto mechanic.




My vehicle is toyota. The problem is when shift in gear that time engine is knocking.That time engine component and bumper is jerking so much. what i will do.
What about a worn balance shaft that makes a clacking noise when you move it side to side and an oil pump going out causing the play to make a loud knocking that sounds like a rod knock. It seems like its not getting any oil and it is amplifying the noise the play makes in the balance shaft. The engine is a v10 triton 6.8l in an F350 Superduty.
My car is a Toyota Altezza 1GFE engine.
i can hear a very loud knock if the car is on idle, just recently I changed the timing belt because it was eaten away buy bad tension bearing and the knock is still there.
what do I do next? please assist.
At first, I need to know Engine Knocking at Idle When Hot or cold. Mainly engine knocking occurs due to the following reasons:
Check out these. Hope you will find your problems and solve this. Have a good day.